Programme
First Phase of Programs:
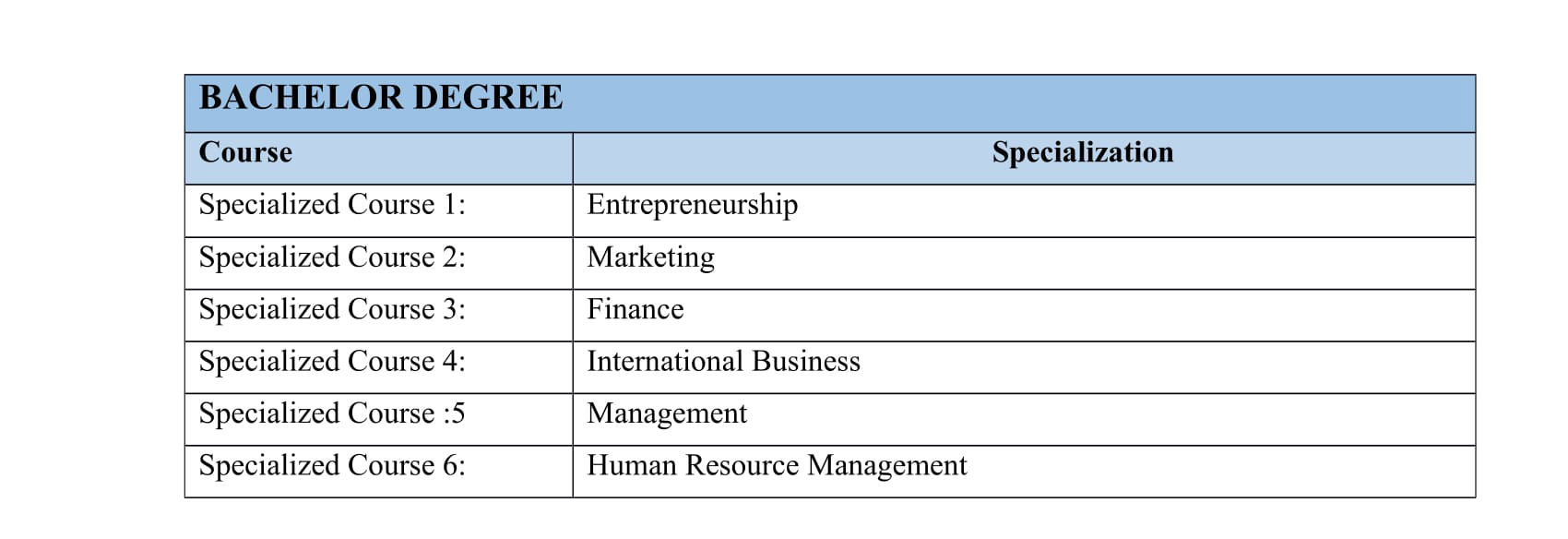
1) Masters in Business Administration:
MBA is a professional 2-year degree program which imparts a strong theoretical foundation in business concepts, provides practical opportunities ( via internships, group assignments and projects) provides a fundamental education in business and management principles. Programs usually allow students to specialize in one of multiple focus areas, including international business, finance, marketing, computer information systems, or accounting. This program can offer practical management training that can prepare students for senior management roles in business. The objective of this program is to develop socially responsive, creative and result oriented management professionals.
BACHELOR DEGREE
Course Specialization
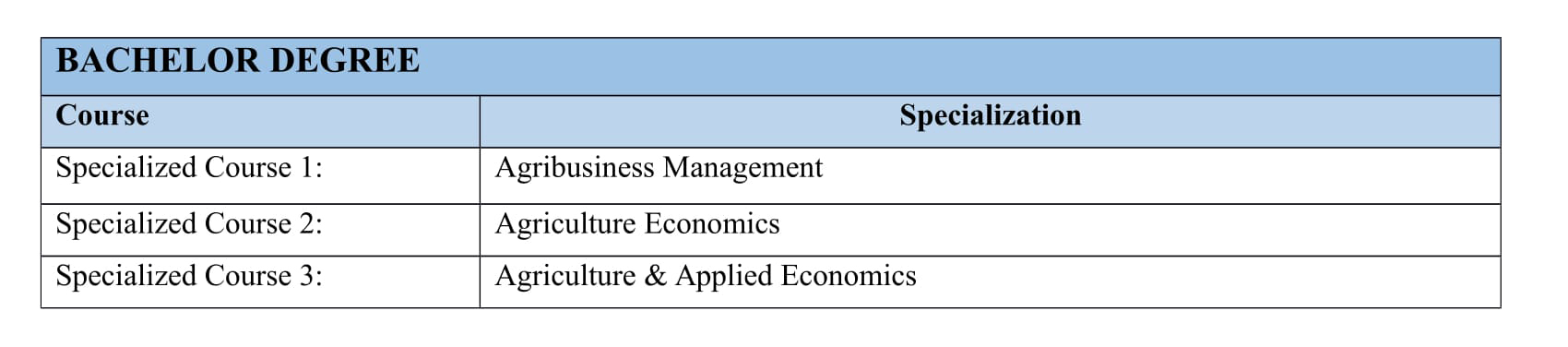
2) Agricultural Economics:
SASORD offers a bachelors degree in Agricultural Business .This program will run under the affiliation of foreign university.
At SASORD, students would learn various skills related to agricultural economics which would help them comprehend economic skills, knowledge and skills related in improving the production of food in the farm. Students would learn the concepts of economics and would further be able to help people in the rural areas to develop their strengths, discover the issues which arise during various steps of farming and solve them economically. The prime objective of SASORD is to enable students get ample career opportunities in various fields in the Agro Industries
BACHELOR DEGREE
Course Specialization
.
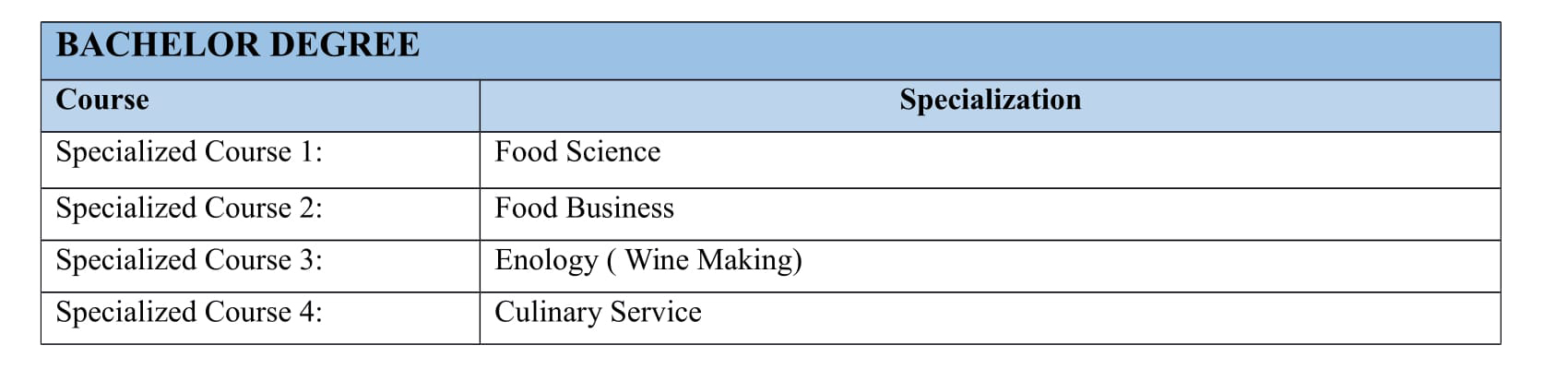
3) Bachelors in Food Science and Nutrition:
SASORD offers Bachelor of Science (BSC) degree in Food Science and Nutrition. This program will run under the affiliation of foreign university.
This degree would enable the students to learn about latest technology involved in manufacturing of food which would develop the normal agro products into the desirable product for a consumer. After graduating from SASORD, the students would be able to pursue their career in various fields of food science as Product Developers, Food Technologists, and Quality Assurance Experts etc.
At SASORD, students would be taught about various scientific disciplines like chemistry, molecular biology, nutrition etc to overcome the challenges which arise in each stage of production of food.
BACHELOR DEGREE
Course Specialization
II) Second Phase of Programs:
1) Bachelor of Science in Development Studies (BSc in Development Studies)
Development Studies is a multi-disciplinary and inter-disciplinary branch of social science that benefits from getting acquaintance with key global, regional and local issues of development such as poverty, rural development, community based natural resource management, governance and communication, disaster risk reduction and management, health and education, agriculture and forestry, climate change and environmental management, gender and inclusion and conflict, peace and human rights among others. The course is designed to prepare critical scholars and skilled professionals to contribute to the development sector at the local, national, regional as well as global level. Students can develop their career in diversified areas such as poverty reduction, entrepreneurship development, public policy and development planning, sustainable agriculture, peace and human rights, natural resource management including the public service in government
What can you do with a degree in Development Studies?
Non-governmental aid organizations: Graduates can work in the developing countries on development projects, or in developed countries running campaigns, lobbying, raising money, and development education. For example see Oxfam and Amnesty International.
International development institutions: Graduates can work with international organizations such as the United Nations, the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, etc.
Government policy: Graduates can work in the public service at all levels developing policy and programs concerning development and aid. For example: working for the Nepal Government in the National Planning Commission or in Aid and Policy Department.
University research: Graduates can continue studying in the university doing postgraduate research, or work as an academic teaching and researching in development studies. For example see: Centre for Development Studies and the National Centre for Development Studies.
Consultancy: Graduates can work as a kind of freelance 'expert' for various organizations on various projects.
2) Development and Environment Economics :
Development and Environment Economics is a newly emerged field of study that has gained popularity within a short time frame because of inclusion of numerous crucial disciplines comprising economics, management of natural resources, quality and climate change. With a focus to preserve biodiversity, this course makes students learn about sustainable way of resource management. Students will have a detailed working knowledge on relevant matters ranging from governance, management to planning.
The ‘Development and Environment Economics’ offers twenty-five modules, where the key subjects are as follows: International Development; International Political Economy; Water Economics and Policy; Management of Natural Resources; Renewable and Non-renewable Resources, Innovation and Technology Management, Local Development Planning Approach in South Asia; A Comparative Perspective; Agriculture, Food and the Environment.
3) Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development:
This course involves various theoretical perspectives on entrepreneurship-innovation-development nexus. It addresses wide range of subject matters that aid in better understanding on trade, management, ethics, leadership and communication. It focuses on enhancing creativity and decision making abilities of students. Students can have an in-depth know-how on creating an innovative strategy, identifying its determinants, developing alternative strategies, and marketing strategy applicable both locally and globally.
The ‘Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development’ offers twenty-five modules, where the key subjects are as follows: Introduction to Rural Technologies; International Trade; CSR Policy and Social Entrepreneurship; Corporate Governance; Business Law and Ethics; Corporate Leadership Development; Business Communication.
4) Environment and Climate Change:
This course comprises of interdisciplinary approaches, which focus on critical challenges impacted in the world due to environmental problems that have threatened the whole planet, the place we live on. The course aims to provide students with a detailed understanding of reasons for climate change, its impacts, and techniques to mitigate them along with a worldwide scenario of the effects climate change has brought among the lives of living creatures and humanity.
The ‘Environment and Climate Change’ offers twenty-five subjects, where the key subjects are as follows: Introduction to Environmental Economics; Renewable Energy for Sustainable Development; International Initiatives to Control Pollution; Mountain Environment and Sustainable Development; National Parks and World Heritage in Nepal; Migration and Environment; Applications of Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Management.
5) Communities, Natural Resources and Management
This course aims to enhance the deeper understanding of the students on the relationship between, communities, natural resources and management. The course is designed to equip students with competencies needed to develop management decisions and policies in relation to managing natural resources in communities. Students will be able to broaden their horizons of knowledge and depict proficiency in community based natural resource management, natural resource policies, administration, planning, and management.
The ‘Communities, Natural Resources and Management’ offers twenty-five modules, as follows: Concept of Communities; Forests and Water in Environmental Quality and Human Well-being; Natural Resource and Conflict Management; Mountain Ecosystem; Integrated Land-use Planning; Organization Behaviour and Human Resource Management; Energy, Environment, and Society.
6) Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security
The course intends to provide students with a detailed understanding and analyses on sustainable agriculture and food security. This course emphasizes on interlinks between food security and agriculture, food distribution system and food supply, food security strategies and marginalized groups inclusive of a widespread subject matter in an agricultural sector including sustainable agriculture.
The ‘Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security’ offers twenty-five modules as follows: Food Security and Agriculture Development Policy in South Asia; Indigenous Knowledge for Sustainable Development; Positive Discrimination Policy and Structural Transformation for Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture; Food Security Governance; Food Behaviour Change an Integral Part of Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture; Eco-Tourism a Means of Food Security for Landless and Small farmers; Climate Change Impacts on Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture.
